Solar photovoltaic system design mainly includes the following contents: 1. Solar photovoltaic system classification; 2. System design information collection; 3. PV design software introduction; 4. Grid-connected system design. This issue is mainly analyzed from two aspects: solar photovoltaic system classification and system design information collection. ""
At present, solar photovoltaic systems are mainly divided into grid-connected photovoltaic systems and off-grid photovoltaic systems.
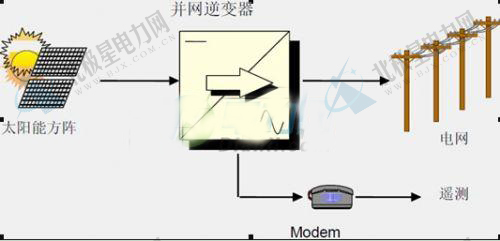
Grid-connected photovoltaic system:
Off-grid (independent) photovoltaic system:
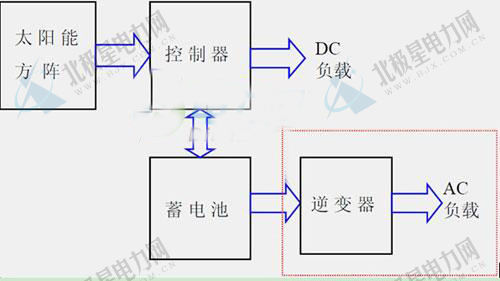
Off-grid (hybrid) system:

Off-grid (hybrid) system:
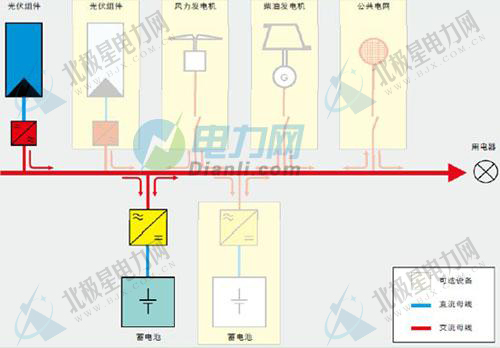
On-grid (hybrid) system:
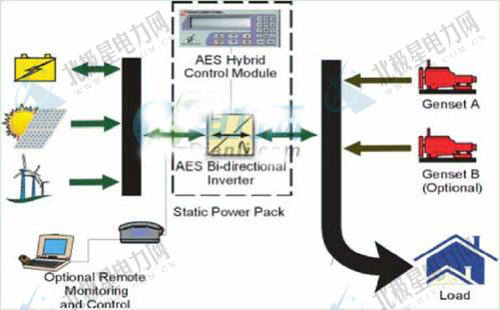
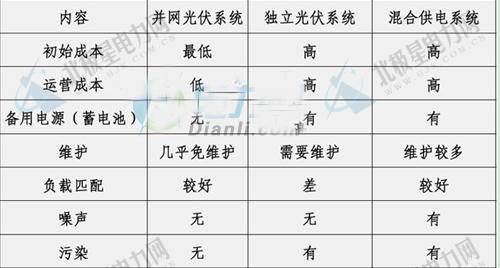
Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of the three systems:
To understand the design of solar photovoltaic systems, we must first understand the principle of solar photovoltaic power generation, its principle is also relatively simple - based on the photovoltaic effect of semiconductors, the use of solar cells to convert solar energy directly to DC power.
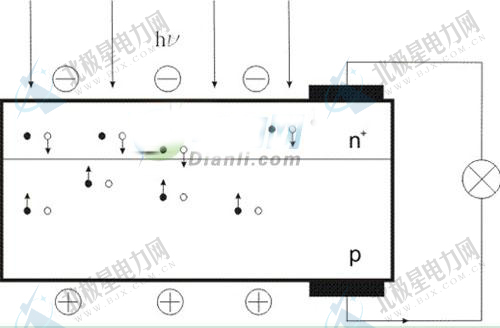
Crystal silicon solar cell schematic
First of all, to introduce the characteristics of photovoltaic power generation, mainly in the following areas:
1, mainly composed of electronic components, does not involve mechanical rotating parts, running without noise;
2, no combustion process, power generation process does not require fuel;
3. There is no exhaust gas pollution in the power generation process, and there is no waste water discharge;
4, equipment installation and maintenance are very simple, simple maintenance, low maintenance costs, reliable and stable operation, long service life of 25 years;
5, adaptability of environmental conditions, can work in different environments;
6. Can work normally and steadily under unattended conditions for a long time;
7. It is easy to expand and expand the scale of power generation as needed.
Second, the photovoltaic power generation system can be divided into the following modes depending on the application and type:
1, to provide power for non-electrical occasions;
2, small-scale solar electronic products;
3, large-scale photovoltaic power generation system;
4. Combined photovoltaic power generation system with buildings (BIPV, BAPV)
Photovoltaic system design information collection mainly includes three aspects: meteorological data collection, location and location information, and related building information collection.
Meteorological data collection also includes solar radiation, temperature, humidity, wind speed and other aspects.
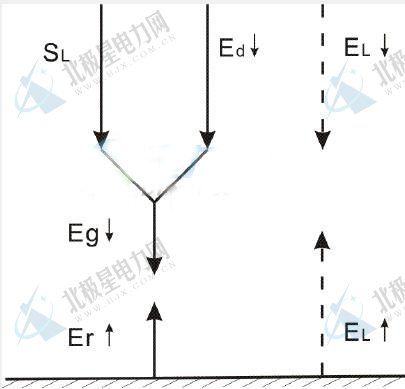
Solar radiation is further divided into solar short-wave radiation (direct radiation SL, scattered radiation Ed, total radiation Eg, short-wave reflected radiation Er), long-wave radiation of the earth (atmospheric long-wave radiation EL↓, ground long-wave radiation EL↑).
The conversion formula between them is as follows: Eg↓=SL+Ed↓; SL=S?sinHA=S?cosZ; E*=Eg↓+EL↓-Er↑-EL↑.
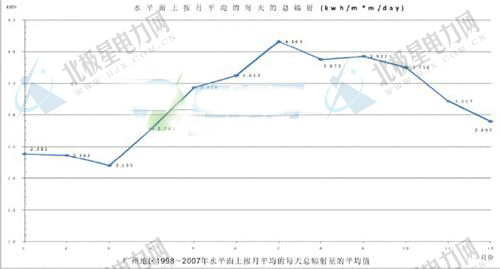
Solar radiation data:
The temperature has three kinds of values: daily average temperature, daily maximum temperature, and daily minimum temperature. The temperature has a great influence on the open circuit voltage, output current, output power, and isoelectric performance of photovoltaic modules, and is an important factor in the subsequent design. It also has a great influence on the environment in which the relevant electrical equipment is used.
Humidity is only one parameter of daily average relative humidity, but it also has a certain influence. Humidity affects the service life of the photovoltaic support and the use of related electrical equipment such as inverters of the photovoltaic system.
The wind speed is divided into the daily average wind speed, the maximum daily wind speed, and the maximum daily wind speed, which are destructive to the photovoltaic equipment. The higher the wind speed, the stronger the destructive power. This also puts forward higher requirements on the wind-resistant safety of the BAPV-mounted PV module brackets and the construction safety of BIPV-installed PV curtain walls, roofs and other structural components.
When it comes to the collection of installation site information, it is mainly affected by the following factors:
1. The orientation of the building at the installation site. In the BIPV system, the orientation of the building usually determines the orientation of the photovoltaic modules, subject to the installation location of the building itself.
2, the installation location of the pass. Whether the PV modules can be delivered to the PV array installation site smoothly; whether the larger devices such as photovoltaic inverters can be smoothly transported to the installation site; if there is no transportation from the building, whether there are lifting conditions.
Installation site information is generally affected by shadows, such as whether the antenna, cooling tower, or railing of the building itself will cause shadow on the PV array; whether the surrounding tall trees or buildings will affect the PV array; It is necessary to take into consideration when installing photovoltaic devices whether there are buildings with larger buildings that will affect the PV arrays, and these problems will have more or less impact on the PV installations.
As for the collection of building information, as long as it is to see whether the building is an energy-efficient building, how the load-bearing capacity of the building installation site such as the roof, the requirements of the building insulation, and the actual building area on the building and the installation of solar photovoltaic modules There are several aspects such as the actual usable area. In addition to the above information, in the installation site information collection, attention should also be paid to the lightning protection grounding in the building; the electrical layout inside the building, such as the layout of the bridge, the location of the power distribution room, etc.; collect the relevant structural drawings; And to understand the relevant requirements of the owner in time, in order to facilitate better construction.