 |
(a) Design and preparation of a hollow-interface microstructured aluminum negative electrode material; (b) Two dual-ion batteries light SIAT; (c) Long cycle stability test of the prepared dual-ion battery.
Recently, Tang Yongbing, a researcher at the Functional Film Materials Research Center of the Institute of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and his research team have successfully developed a metal aluminum foil negative electrode material with a hollow interface structure, which has been applied to high-efficiency, low-cost dual-ion batteries. This new structure effectively solves the problem of poor volume expansion and poor cycling performance of low-cost metal anode materials during charge and discharge. Relevant research results: "Ultra-stable solid electrolyte layer formed by foam paper-like interface design with an Ultrastable Solid Electrolyte Layer for High-Performance Dual-Ion Batteries" Has been published online in "Advanced Materials" (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201606805, IF = 18.96).
With the rapid development of the market size of portable electronic devices and electric vehicles, the demand for high-energy density, low-cost secondary batteries has become increasingly urgent. At present, commercial lithium ion batteries are mostly made of graphite anode materials, the theoretical specific capacity is only 372 mAh g-1, and the compact density is low, which limits the further increase of energy density of lithium ion batteries. By alloying/dealloying with lithium ions, inexpensive metal anodes generally have a larger specific capacity and are expected to achieve higher energy densities. Among them, the theoretical specific capacity of aluminum is as high as 2234 mAh g-1 (Li9Al4), and its reserves are abundant and the price is low. However, the aluminum negative electrode will have a certain volume expansion during the battery reaction, thereby affecting the cycle stability of the battery.
Based on the above considerations, Tang Yongbing and his team members Qin Panpan, Wang Meng, Li Na, and others successfully developed a metal aluminum foil material with a hollow interface microstructure, and at the same time, it integrated the active material and current collector and designed it. Successfully applied to new high-efficiency, low-cost dual-ion secondary batteries. The structural design and the modified aluminum foil are used as the negative electrode active material and the current collector. The expanded graphite is a positive electrode and a conventional electrolyte is used. Compared with traditional lithium-ion batteries, the new secondary energy storage battery has a higher operating voltage (average discharge voltage of ~4.2V), while significantly increasing the proportion of active material and energy density, and significantly reducing the manufacturing cost, and Environmentally friendly. In addition, the interface design of the hollow microstructures makes the lithium-aluminum alloy region successfully confined to the hollow interface, thereby effectively alleviating the volume expansion of the aluminum negative electrode during the alloying process, and obtaining a highly stable SEI film. The results show that the new battery circulates for 1500 cycles at a charge-discharge rate of half an hour (2C), and the capacity retention rate is as high as 99%. In addition, even at a power density as high as 2113 W kg−1, the battery has an energy density of 169 Wh kg-1 (10C, charge and discharge time is 6 min) is much higher than most commercial lithium-ion batteries. The research results have guiding significance for the development of cheap metal anode materials and are expected to promote the development of high-energy, low-cost secondary batteries based on inexpensive metal anodes.
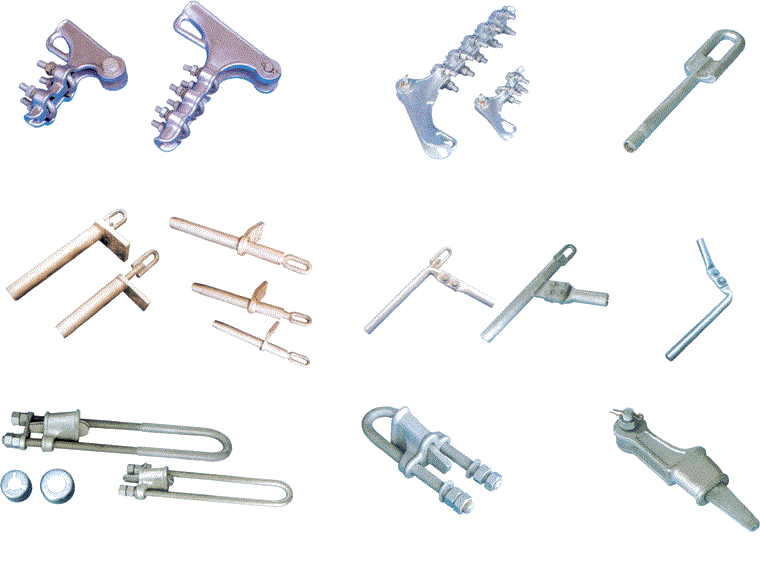
Strain clamps are used to fix conductors and ground wires to insulators or link fittings to tower arms and substation structures.
There are two basic systems of strain clamps,
1. Detachable clamps, such as wedge-type tension clamps, thimbles, bolted type tension clamps, which allow for subsequent adjustment.
2. Non-detachable clamps, such as compression dead-end clamps which require absolute matching to the conductor length.
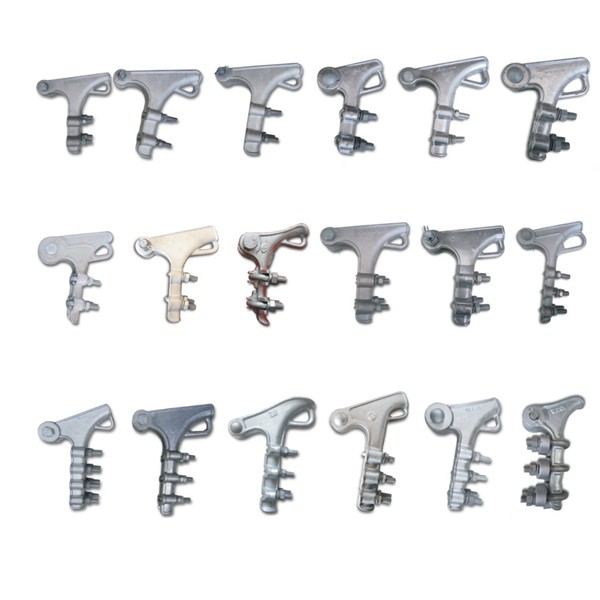
Main type of the strain clamps
1-NY Hydraulic Strain Clamp for Conductor ( bolted type )
2-NY-G Compression Strain Clamp for Steel Wires ( welding type )
3-NY-G Compression Strain Clamp for Steel Wires ( forging types )
4-NZG Strain Clamp ( hydraulic compression type )
5-NY-N Strain Clamp for HRAAS Conductor ( hydraulic compression )
6-NY-BG Strain Clamp for ACSR/AS Conductor ( hydraulic compression )
7-NLL Aluminum Alloy Strain Clamp ( bolted type )
8-NLD Malleable Iron Strain Clamp ( bolted type )
9-NLZ Deadend Strain Clamp ( bolted type )
10-WNY Strain Clamp
11-NY-H Aluminum Alloy Strain Clamp
12-NY-HG Aluminum Alloy Strain Clamp


If you have any questions, please contact with us directly.
Our company is solemnly committed to the majority of customers: reasonable price, short production cycle, considerate service. We look forward to cooperating with you.
Strain Clamp
Strain Clamp,Aluminum Alloy Hd Strain Clamp,Strain Cable Clamp,Aluminum Alloy Strain Clamp
Shandong Vantage International Trade Co., Ltd. , https://www.steelplate.be