During the whole process of canning, due to the temperature changes in the tank required by the process, as well as the specific operating conditions and accidental factors in the production, the pressure in the tank will be normal and possible abnormal changes, resulting in vacuum at the production site. Not enough, quality problems such as expansion irrigation. To analyze the reasons, it is necessary to understand the various factors related to the vacuum tank acquisition knowledge and pressure changes, and to find the root knot according to the site process conditions.
First, the reasons for the food tank vacuum to obtain
The food canning process requires exhaust seals, a certain degree of vacuum has been obtained, and the contents are better protected. The reasons can be summarized as follows.
1, to oxygen defense bacteria. The survival and growth of microorganisms require oxygen. Although the oxygen demand of various aerobic bacteria is different, their growth can be effectively controlled under low-oxygen conditions. Even anaerobic microorganisms or facultative anaerobic microorganisms, life activities are also Need oxygen. And the exhaust vacuum is also an effective measure to reduce bacteria.
2, to oxygen preservation. When food is exposed to the air, it is extremely prone to oxidation and destroys food taste. Exhaust deoxygenation apparently effectively creates an oxygen-deficient environment and guarantees the original taste of the food.
3, to oxygen protection. The preservation of vitamins is a daunting task for food cans. Do everything to reduce the damage of vitamins. Experiments have shown that in the presence of oxygen, when heated to above 1000C, vitamins are gradually decomposed, but vitamins are relatively stable under anaerobic conditions. Vitamin C, which is most easily destroyed, is virtually free from damage even under pasteurization vacuum.
4, to oxygen tank. Corrosion of the inner wall of the can, if oxygen is present, exacerbates electrochemical corrosion. This electrochemical reaction of tinplate cans is a cathodic reaction. 2H++1/2O2+2e→H2O can generate water without generating hydrogen, thus promoting the anode reaction: Sn→Sn++2e promotes the corrosion of tin.
In the absence of oxygen, the cathode reaction is very slow: 2H++2e→2H2→H2↑, the anodic reaction is slow, and tin corrosion is also slow.
Obviously in an oxygen-free environment, the corrosion of the tank wall slows down, protecting the life of the tank.
5, to prevent tank convex. When the cans are sealed by high-temperature sterilization, there is a possibility that the air may be thermally expanded to produce can-convex phenomenon due to the food and steam existing in the cans. In severe cases, the double-wrapped structure is loose or leaks. In Kawaguchi, Japan, a comparative experiment was conducted. The two types of cans sealed at high temperature (700C) and low temperature (310C) were lower in pressure at the same sterilization temperature (1100C). The difference was:
16.6×104Pa?11.5×104Pa≈5.0×104pa
This actually shows that the cans that get vacuum through the exhaust will have less overpressure in the tank during heating and sterilization, and may avoid undesirable phenomena such as suction caps, suction angles, detachment, deformation, cracking, and the like. Relatively speaking, good cans that are well vented are beneficial for choosing higher sterilization temperatures to increase the sterilization rate or increase productivity.
Second, food cans vacuum access method.
From the above analysis, we can see that the essence of food can vacuum is to remove oxygen from the exhaust, not to achieve vacuum. Currently there are four main methods for canned oxygen removal from cans:
1, heating exhaust method. The hot food is put into the tank, or the can is heated through the exhaust box, and the air is expanded by the expansion of food steam and air in the tank. With the increase of the proportion of water vapor in the gas, the oxygen is relatively reduced, and the hot water is sealed immediately. After cooling, a certain degree of vacuum is formed.
Here should pay attention to the food temperature, tank temperature and exhaust time control, according to the actual conditions of food products, tank size, tank capacity materials, etc., the temperature should be based on the center of the canned, exhaust time to exhaust effect and maintain The principle of comprehensive food quality care.
2, vacuum sealing tank exhaust method. In the sealing process, the vacuum pump is used to extract the gas in the seal to form a certain degree of vacuum. When the can enters the sealer to seal the vacuum chamber, the gas in the tank escapes immediately and seals quickly, resulting in a certain vacuum in the tank. degree. It is often used for foods that are not suitable for heating.
Here we must pay attention to the degree of vacuum sealing, and the time for the cans to enter the sealed chamber to seal the cans, so as to avoid the problem of tank overflow and insufficient exhaust.
3, steam injection exhaust method. After the cans have been pre-sealed, the air in the headspace is replaced by the injection of steam into the headspace of the cans, and the air is immediately sealed. The headspace is filled with mainly steam and a vacuum is obtained after condensation. Therefore, the injected steam must have a certain pressure and temperature, and the entire injection must be continued until the roll is sealed. This method should pay attention to the canned headspace, generally 8 ~ 10mm, the temperature of the canned food is increased, which is conducive to a higher degree of vacuum. As shown in Figure 1, the test data for the United States Ketchup No. 2 cans (532 lm cans) has a tip clearance of 9.53 mm. 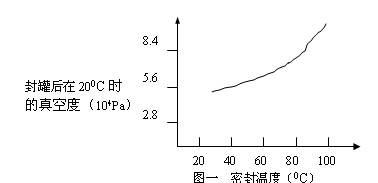
4, gas replacement exhaust method
The method of filling the canopy with suitable protective gas into the headspace to replace the original air is similar to the principle of steam injection, except that the injected gas is not steam but protective gas such as CO2, N2, etc.
Third, on the food tank low vacuum or expansion tank problem analysis
The occurrence of a low vacuum or expansion tank in the food cans indicates that the pressure in the cans is not within the normal range. This phenomenon is mostly a quality problem. The moderate expansion tanks in the heat sterilization process are in the normal range. There are many reasons for quality problems, so it is important to carefully analyze the many factors that cause pressure buildup and changes in the tank.
1. Influence of contents on pressure changes
There are three influencing factors on the pressure of the contents. The first is the thermal expansion property of the contents. Since the expansion coefficients of different contents of foods and the like are different, the increment of the volume varies with the increase of temperature, and the volume of the empty cans has certain conditions. Next, the reduction of the headspace volume will be different, reflecting the different pressure changes. The second food tissue often contains non-condensing gases that escape when heated and thus can affect the pressure inside the can. The amount of escape is also related to the nature of the food. The third content is often a multi-ingredient blended food. The filling process is often accompanied by bubbles, which may also escape during the heating process and affect the pressure inside the can. The amount of entrainment is related to the specific process.
It can be seen that the contents themselves are important factors affecting the pressure change in the tank. The first and second factors are objective physical factors. The performance and laws should be grasped through test experiments. For example, the specific volume of water is 1.0018cm3 at 200C. /g, 1200C is 1.003cm3/g, the third factor is to grasp the stable process, so that the contents of the uniform, stable filling.
2, the impact of canned containers on pressure changes
There are three factors that affect the pressure change of the canned container. The first is the material of the container, which determines its expansion coefficient. The second is the geometric parameters of the tank, including the empty tank diameter, height, thickness of the tank, directly determines the empty tank volume, and these parameters are different in the heating rate of volume change is not the same, reflecting the pressure change is not the same. The third is the empty can structure, which includes the can body and the ribs of the can lid, etc. They enhance the strength and elasticity of the can body and ensure the stable relationship between volume and pressure.
3, the impact of temperature on pressure changes
The effects of the above-mentioned contents and empty container on the pressure are all based on the temperature change, and the change of the temperature condition can be seen from the canning process in three different periods.
The first is the sealing temperature. For example, the high-temperature sealed cans are lower than the low-temperature sealed cans, and the pressure generated in the cans at the same sterilization temperature is lower because the high-temperature sealed exhausting effect is good. The second is the temperature of pasteurization, which is not only accompanied by the expansion of the content and volume of the container, but is often a change in the volume of the contents that is greater than the change in the volume of the container, resulting in an increase in pressure, and the expansion of the headspace gas and the escape of the contents gas. The vaporization of moisture causes the pressure in the tank to increase, and the excess pressure is calculated as
P3 =P2?P1=(p steam'' ?P steam')+P gas'(V1Ts/V2Tso?1)
P3 in the formula is the difference between the pressure in the tank during sterilization (P2) and the pressure in the tank during sealing (P1).
"P Steam", "P Steam" - Steam Pressure at Sterilization and Sealing
P Steam' - air pressure during sealing
V1, V2 - Headspace Volume in Tank during Sealing and Sterilization
Ts0 TS - air temperature during sealing and sterilization
The formula shows that high sealing temperature Tso can reduce excess pressure, while high sterilization temperature increases excess pressure. The third is the cooling temperature. After the sterilization, the cooling temperature is too fast. Since the pressure outside the tank rapidly decreases, the pressure in the tank decreases slowly, and the pressure difference rapidly increases. At this time, the tank is most likely to be deformed. Therefore, the counter-pressure cooling method is often adopted. That is, after the heating of the steam is stopped, high-pressure air or water is injected into the sterilization pot, and the pressure or the water is adapted to the pressure in the tank to avoid deformation of the can.
4. Effect of loading of internal contents on pressure changes
The filling level of the contents is the ratio of the volume of the contents to the volume of the empty cans;
F1 = V food '/V can'
It directly determines the size of the headspace and influences the volume change during heating:
V1/V2=(1-f1)/(xyf1) In order to control the change of the headspace, it can be known from the equation that for a tin can, when the degree of food expansion y is less than the degree of expansion x of the can container, f1 must be increased. When >x, f1 should be reduced.
Through the above analysis, we can summarize the following points about the pressure changes in the tank:
1), to improve the sealing temperature of canned foods, can reduce the degree of expansion of the food when heating sterilization, you can reduce the pressure inside the tank.
2) In order to control the volume change of the tinplate can during the canning process, an anti-pressure sterilization method may be adopted.
3) For container and food expansion x and y, under certain conditions, pay attention to the appropriateness of the filling level f1 of the content, that is, when x>y, f1 can increase the point, and x, f1 should decrease.
4) Improve the structure of the canned container, increase its compressive strength, and obtain elastic adaptability, so as to obtain a V2 effective accommodation space for the top clearance volume in the can during sterilization.
5) Improve exhaust efficiency, improve exhaust method, and fully reduce air pressure P'gas.
A Robe hook is a great way to hang bath towels and clothing to dry, and they aren't just for the bathroom. They are also great storage solutions for entryways, laundry rooms, kitchens, and bedrooms.
Robe Hook,Robe Hook Design Ideas,Wall Mounted Robe Hook,Double Robe Hooks
Kaiping Jenor Sanitary Ware Co., Ltd , https://www.sanitaryjenor.com