1. Overview of Advanced Energy Materials: Latest Developments and Prospects of Layered Electrode Materials for Lithium Batteries
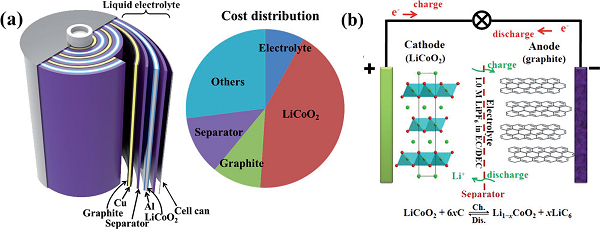
Figure 1 Structure and relative cost of each component
Since the commercialization of lithium batteries, they have been widely used in portable digital products. However, the energy density and power density of lithium batteries are insufficient to meet the growing demand. It is extremely urgent to explore cathode/anode materials with good rate performance and long cycle life. Recently, Professor Tao Zhanliang and Shu-Lei Chou (co-communication author) from Nankai University summarized the research progress in hierarchical structure electrode materials in recent years, and discussed in detail the influence of hierarchical structure on electrochemical performance. In addition, the authors also presented the challenges and application prospects of layered electrode materials.
2. Overview of Advanced Energy Materials: Application of Gel Polymer Electrolytes in Electrochemical Energy Storage
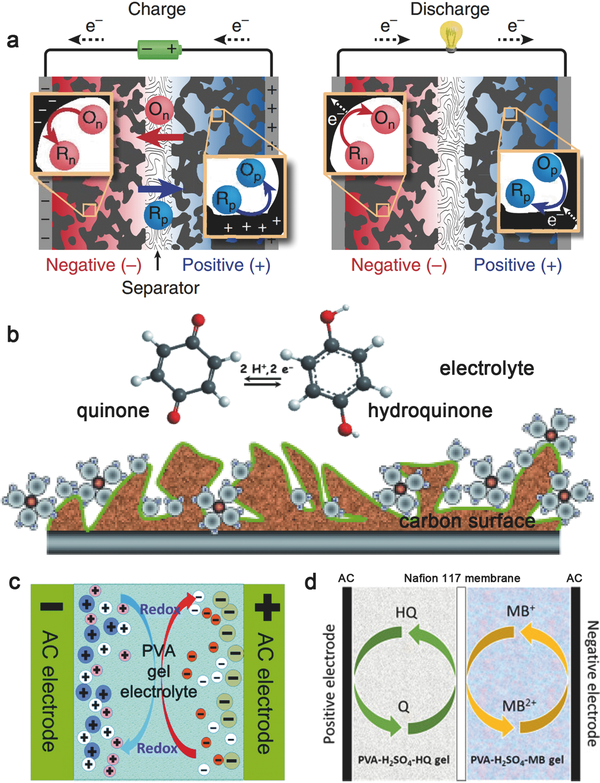
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of battery charging and discharging process
While flexible wearable electronic products are booming, their safety issues and operational stability have caught the attention of the world. Compared to conventional liquid electrolytes, gel polymer electrolytes (GPE) have higher safety and adaptability to flexible energy storage device designs. Recently, Professor Peng Huisheng (corresponding author) from Fudan University outlined the application of gel polymer electrolytes in electrochemical energy storage. This paper discusses how to prepare a functional GPE that has a uniform amount of lithium ion migration and provides additional dummy capacitance for the entire capacitor. The most notable of these is the intelligent gel polymer electrolyte with self-protection, heat resistance and self-healing ability. In addition, the authors have made a prospect for the future development of electrochemical energy storage devices.
3, Angewandte Chemie International Edition review: 3D laser micro and nano printing technology
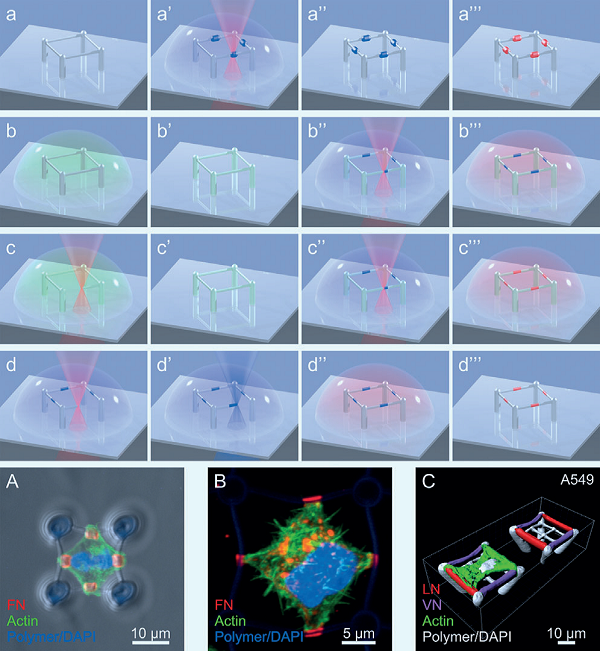
Figure 3 Spatially functional three-dimensional micro-stent
Recently, Christopher Barner-Kowollik from Queensland University of Technology and Martin Wegener (co-communication author) of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and others have summarized the latest research progress in 3D laser micro and nano printing technology. 3D printing technology has evolved from advanced functional materials for cell biology and electronics to the need to overcome chemical barriers to achieve fast write speeds with resolutions below the diffraction limit. The authors achieved laser direct writing of a variety of materials in a resist by a highly wavelength selective (λ-orthogonal) photochemical process. Finally, the authors describe adaptive 3D structures that respond to external stimuli such as light, heat, pH or specific molecules, and propose advanced concepts for degradable scaffolds.
4. Advanced Materials Review: Mechanical Properties of Metal-Organic Frameworks
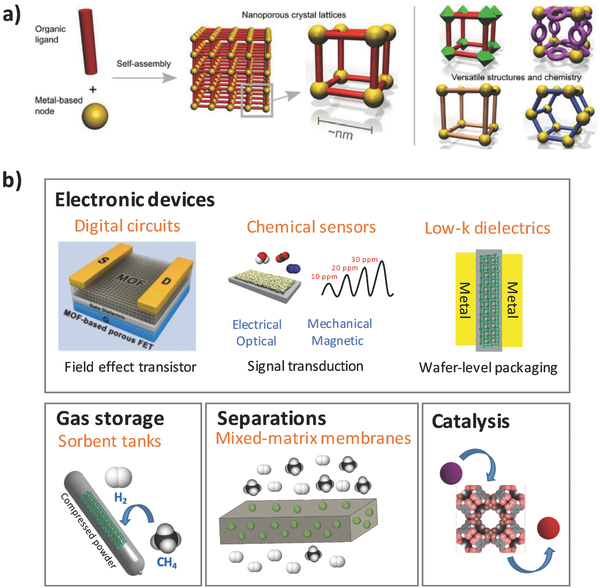
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of metal organic frame structure
The metal-organic framework (MOF) is characterized by an inorganic-organic hybrid nanoporous structure to improve its mechanical properties. Recently, Nicholas C. Burtch and Mark D. Allendorf (co-communication author) from Sandia National Laboratory and others outlined the new opportunities and challenges brought about by the function and technology application of metal organic framework (MOF) equipment. The authors discuss in depth the application of MOF as a functional nanodevice and the recent advances in MOF mechanical structure-performance changes due to properties such as defects and interpenetration. In addition, the authors discuss the latest algorithms for quantifying the mechanical properties of MOF.
5. Progress in Polymer Science: Preparation and Structural Characterization of Thermoplastic Vulcanizates
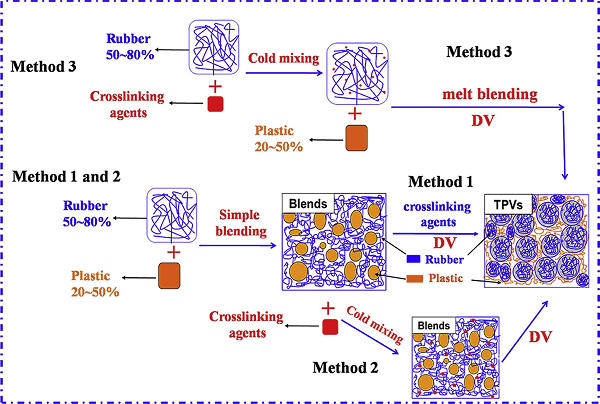
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the preparation method of thermoplastic vulcanizate
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) consist of a high content of crosslinked rubber as a dispersed phase and a low content of thermoplastic as a continuous phase, typically prepared by dynamic vulcanization of a preblended rubber phase and a plastic phase. Thermoplastic vulcanizates are a class of high performance thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) that have attracted a lot of attention from scientists because of their excellent elasticity and mechanical properties of crosslinked rubbers, as well as the good processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. Recently, Professor Zhang Liqun and Prof. Tian Ming from Beijing University of Chemical Technology (co-author) and others summarized the latest research progress of TPV preparation methods, as well as the formation mechanism and influencing factors of TPV microstructure. The authors provide new ideas for the preparation of high performance TPV materials.
6. Advanced Materials Review: Energy Storage and Conversion of Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Composites
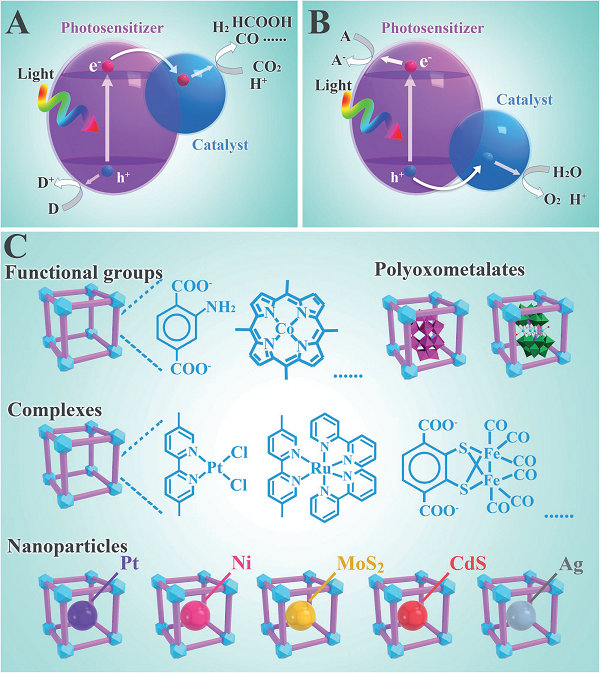
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of the photocatalytic system
Recently, Professor Xu Qiang from the Japan Institute of Industrial Technology and Professor Zou Ruqiang from Peking University (co-author) and others summarized the latest developments in metal-organic framework MOF and its composite materials in energy storage and conversion applications, including photochemistry and electricity. Chemical hydrogen production, CO2 reduction and water oxidation, supercapacitors, lithium-ion batteries, Li-S batteries and Li-O2 batteries. The authors delve into the design of metal-organic frameworks and their composites (for example, the combination of active components, the design of smart forms, and the choice of organic connectors and metal nodes) for specific energy storage and Transform application areas. Finally, the authors present recent research advances that will contribute to the development of MOFs and MOF composites in advanced energy storage and conversion applications.
7. Chemical Society Reviews: Chemical process assisted low temperature crystallization of metal oxide films
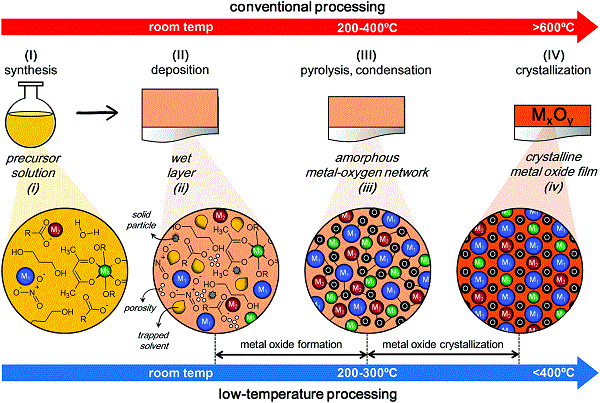
Figure 7 Schematic diagram of the formation process of crystalline film
With the continuous development of low-temperature processing technology for metal oxide thin films, oxide layers (amorphous semiconductors) can be directly integrated on low-melting polymer substrates for flexible electronic systems, which increases economic benefits while reducing energy consumption. . However, higher crystallization temperatures (> 600 ° C) hinder the development of oxide functional devices. Recently, Iñigo Bretos and M. Lourdes Calzada (co-author) and others from the Royal Institute of Madrid outlined a new method for inducing crystallization of metal oxide films at low temperatures based on wet chemical methods. The key to the preparation process is the formation of defect-free, highly densified amorphous metal oxides in which light can be used as a complementary source of energy for inducing crystallization.
8. Chemical Society Reviews: Application of dendrimers combined with natural products on anticancer agents
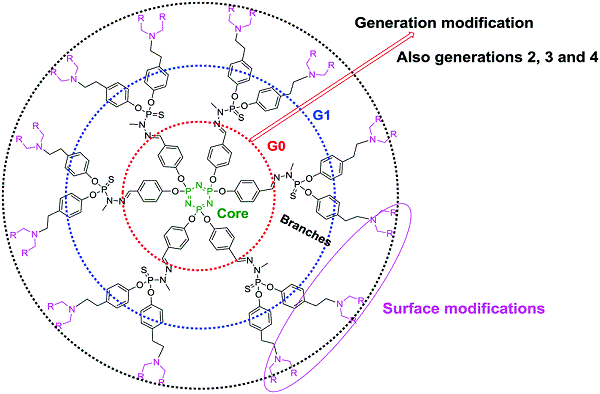
Figure 8 2D chemical structure of dendrimers
In the field of nanomedicine, due to the adjustable range of nanoscale structures, nanocarriers are not only used for drug delivery, but also for gene delivery and imaging agents, tissue targeting, and tumor therapy diagnosis. The types of nanoparticles used clinically are mainly organic nanoparticles such as liposomes, protein groups, polymers/micelles, and inorganic nanoparticles such as iron oxide, silicon dioxide and gold. However, there are few reports on the use of natural products as nanocarriers. Recently, Serge Mignani from the Fifth University of Paris, João Rodrigues of the University of Madeira, and Jean-Pierre Majoral of the French Scientific Research Center (co-author) and others outlined the new materials in which dendrimers are combined with natural products. Application on cancer agents. The biggest advantage of using dendrimers in nanomedicine is its high biocompatibility and good water solubility. The use of new materials can effectively reduce the intrinsic toxicity and side effects of anticancer agents, improve the therapeutic effect, and thus reduce patient dependence.
9. Overview of Accounts of Chemical Research: Simulation Study on Electrochemical Stability and Interface Structure of Battery Electrolytes
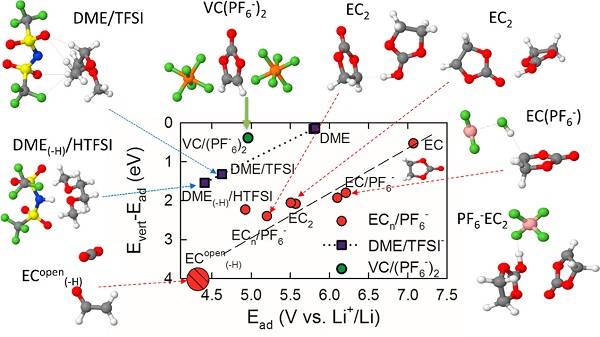
Figure 9 H transfer reaction during oxidation
Recently, Oleg Borodin (corresponding author) and others from the US Army Research Laboratory reported the observation of solvent and ion distribution on the molecular scale of the electrolyte bilayer, and used the function of potential to predict electrolyte stability and its initial oxidation and reduction reactions. The change. Through molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, the authors found that anions can be designed to preferentially desorb from the positive electrode or desorb from the increased electrode potential, providing additional leverage to determine the order of anion oxidation and effectively select the sacrificial anion to decompose. . In addition, the authors confirmed the reverse electroadsorption behavior of sulfonimide (TFSI) and triflate (OTF) in high-concentration aqueous electrolytes by surface-enhanced infrared spectroscopy.
10. Overview of the Accounts of Chemical Research: Mechanical Stability of Metal-Organic Frameworks
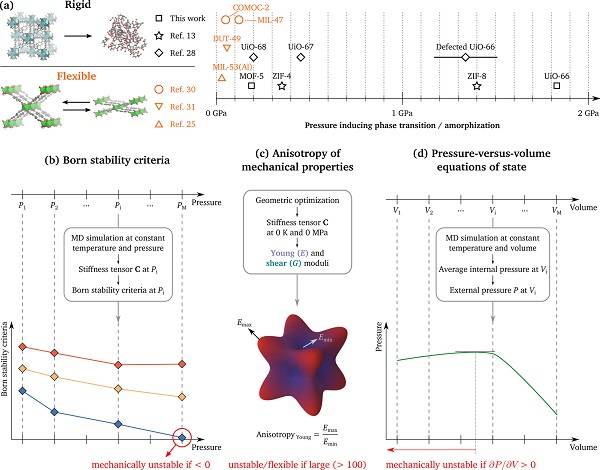
Figure 10 Critical pressure of metal-organic framework induced phase change or amorphization
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) consist of inorganic moieties interconnected by organic ligands to obtain the desired structural and chemical characteristics by functionalizing or substituting these structural units. Recently, Veronique Van Speybroeck (corresponding author) and others from Ghent University outlined recent advances in the computational characterization of the mechanical stability of MOFs. Three calculation methods are proposed in this paper, which are the Born stability criterion, the anisotropy of mechanical modulus and the volume equation of the pressure versus state. The results of the study show that the state pressure-volume equation can be used to mitigate the effects of these transient fluctuations, resulting in more accurate results.
11. Chemical Reviews: Crystal Growth Studies with Polymer Additives
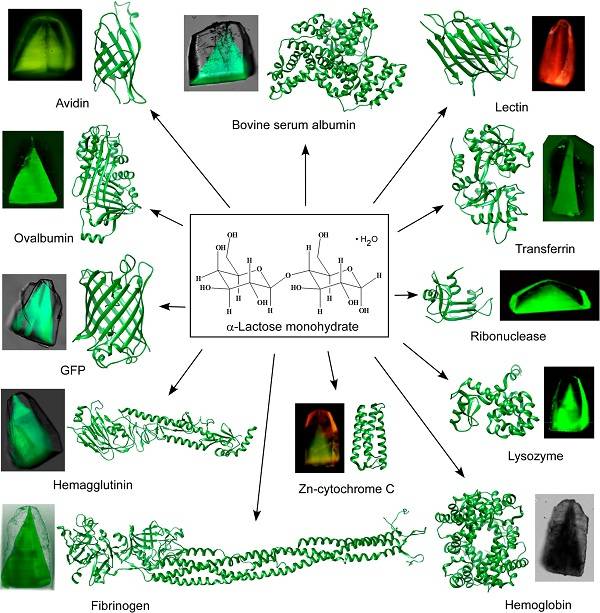
Figure 11 Schematic diagram of crystal structure
The interaction of macromolecules with the surface of growing crystals plays an important role in biomineralization, which can determine whether some organisms survive at low temperatures, and has good prospects in industrial applications. Recently, Alexander G. Shtukenberg (corresponding author) and others from New York University outlined the crystal growth mechanism in the presence of macromolecules including peptides and proteins, focusing on the interactions between macromolecules and crystal material surfaces. Macromolecular adsorption on the surface of the type crystal and crystallization kinetics in the presence of macromolecules. Throughout the process, the adsorption and binding selectivity of macromolecules on the surface of the crystal was studied in depth. In addition, the authors explain the special effects of macromolecular size and complexity by comparing them with other crystallization additives.
Tool belt is a piece of equipment used to hold and organize tools for easy access during work. Tool belts are commonly used by construction workers, carpenters, electricians, and other tradespeople who need quick access to their tools while working.
A typical tool belt consists of a belt made of leather or nylon with pockets or pouches attached to it. The pockets or pouches are designed to hold different types of tools, such as hammers, screwdrivers, pliers, and measuring tapes.
There are different types of tool belts available, including leather tool belts, nylon tool belts, and electrician tool belts. Some tool belts also have suspenders or shoulder straps to help distribute the weight of the tools more evenly and reduce strain on the back.
When choosing a tool belt, it is important to consider the type of work you will be doing and the types of tools you will need to carry. You should also consider the size and fit of the tool belt to ensure it is comfortable and does not interfere with your movements while working.

Tool Belts,Electrician Tool Pouch,Tool Pouch,Small Tool Bag
ZHANGJIAGANG CITY XIANGLE TOOL CO., LTD. , https://www.xiangletoolbag.com