
It seems that the exchange rate is a price issue. In fact, there are very complicated factors behind it. The exchange rate usually reflects the development of the entire economy and the performance of all policies, especially the RMB exchange rate. Once the trend is formed, it is often A long period of time, not a short period of time (see the picture below).
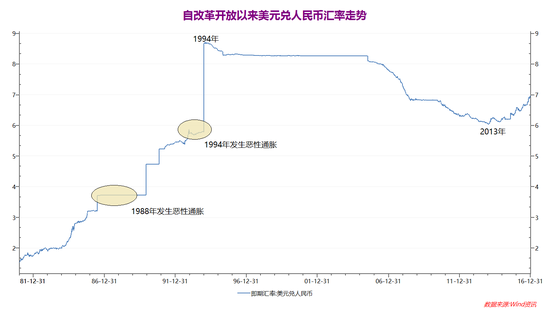
From the perspective of China's economic development, the depreciation of the RMB exchange rate from 1978 to 1994 is in line with the revaluation demand of the Chinese economy from the planned economy to the market economy; the appreciation from 1994 to 2013 is also in line with China's rapid economic development and trade. The fact that capacity is rapidly expanding.
From the current situation, the structure of China's economy is changing, and the domestic asset price is generally overvalued. This round of RMB depreciation since the beginning of 2014 is not a technical depreciation. The exchange rate against the US dollar may even last for five. Years and ten years. But this does not mean that the Chinese economy has weakened since then. Just like the depreciation of the RMB exchange rate from 1978 to 1994, it does not mean that the Chinese economy has a problem, but it is precisely the need of China's economic development.
However, it should be noted that since the reform and opening up, China has experienced two of the most serious hyperinflation, both of which occurred during the depreciation of the RMB exchange rate. One was in 1988 and the other was in 1994. In the past two years, the inflation rate in the Chinese market reached 18.8% and 24.1% respectively.
The current factors affecting the depreciation and speed of the RMB are, on the one hand, expected. As the exchange rate of the RMB against the US dollar has depreciated by 2.4%, 4.8% and 6.8% respectively in the past three years, this progressive depreciation has formed an inertial expectation. It is widely expected that the depreciation of the RMB in 2017 may be higher than in 2016, and the impact on the exchange rate is expected to be greater. On the other hand, with the contraction of US monetary policy, all major currencies in the world are in the channel of depreciation against the US dollar. In addition, China’s economic growth has declined significantly, investment returns are expected to decline, and the ability to attract foreign investment has weakened. Weakness is a normal thing.
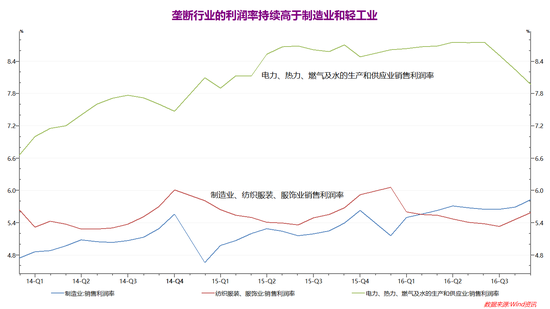
China is a country with an increasing proportion of exports to GDP. In 2010, exports accounted for less than 10% of GDP. By 2015, this figure had become 22%. China's manufacturing industry has a profit margin of less than 6% (below the profit margin of nearly 8% in monopoly industries such as electricity, heat, gas and water). If the RMB exchange rate is not depreciating, but appreciation, the entire export-oriented manufacturing industry will not be able to create. What profit.
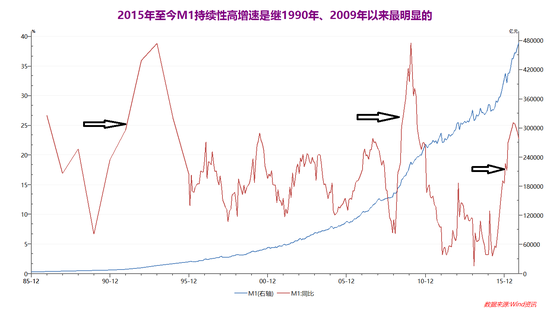
Looking back, the RMB exchange rate has not depreciated at the stage of depreciation. For example, from July 2008 to June 2010 after the outbreak of the subprime mortgage crisis, the world is trying to stimulate exports. China has also launched “four trillionâ€. The stimulus plan, but in order to stabilize the financial market, the renminbi even adopted a fixed exchange rate with the US dollar. During this period, the euro and the British pound depreciated by 20% and 30% respectively against the US dollar. During the same period, the external appreciation of the renminbi and the depreciation of the renminbi were very obvious. This caused the price of the real estate market to soar and the cost of the real economy to increase rapidly. Especially in the case of weak external demand and a strong exchange rate of the renminbi, the export-oriented manufacturing industry could not survive. The comprehensive "de-reality" of the Chinese economy began at that time.
Another data is that, in the context of the renminbi-dollar exchange rate fell by 4.8% in 2015, according to the calculation of the Bank for International Settlements, the nominal effective exchange rate of RMB rose by 3.66% in 2015, and the real effective exchange rate appreciated by 3.93%.
The exchange rate is only a figure for the ordinary people, but for a country's economy, it is a big game. For example, an economy like Switzerland that is mature and has a very high credit rating. According to the Swiss "Sunday", in 2014 the Swiss National Bank spent an average of 1.2 billion Swiss francs per week to drive down the exchange rate. During the Brexit period, the British pound once fell more than 10%, but the Bank of England made it clear that it will not interfere with the pound's decline. Bank of England Deputy Governor Ben Broadbent said in October last year that the British four-month sterling since the Brexit vote The sharp decline experienced has served as the UK's economic shock absorber, and the devaluation of the pound has helped support the economy.
Since the Chinese foreign exchange market is not fully open, the overall exchange rate fluctuations are still very small. The general public does not have much concept of exchange rate fluctuations (the fluctuations of other currencies are much higher than the RMB), and the policy-level regulation has intensified this. Panic, the people are more likely to respond to the expectation of depreciation. I am not in favor of competitive devaluation here, but at least the lowering of the RMB exchange rate should be considered from the perspective of the redistribution of wealth between countries. The distribution of wealth between countries is trade on the one hand and the exchange rate on the other. If the exchange rate is not handled well (strong support), trade will be greatly affected.
From a longer-term perspective, what the people really worry about is not the depreciation of the exchange rate, but the mistrust of the purchasing power of the renminbi caused by various reasons. If the domestic real estate market bubble is still difficult to suppress, all kinds of prices will rise, If the stock price and other asset prices are not moving, a roller coaster market will come. Even if the RMB exchange rate does not depreciate, many investors will find ways to exchange foreign exchange and hold international assets.
Production name
High quality Die cutting heat resistant adhesive polyimide masking tape
Material
Polyimide film + Silicone adhesive
Usage
widely widely used in high temperature masking protection in electronics industry
Feature
♦Powder coating protection
♦Glass sandblasting protection
♦Paint spray protection
♦Ordinary surface protection
♦ Silicone Adhesive Heat Resistant High Temperature Polyimide Tape
♦ High temperature, solvent resistant, stable and reliable
♦ Easy peel off no glue residue
♦ H-class insulation
♦ Suitable for pcb 3d printing and transformer insulation
♦ Strong tensile strength
♦ Offer sheet or roll material or diecut processing.
Advantage
1.Factory supplier: Silicone Adhesive Heat Resistant High Temperature Polyimide Tape
2.Competitive price:Factory direct sales, professional production, quality assurance,
3.Perfect service:Delivery in time,and any question will be replied in 24 hours
Punching Tape,Punched Paper Tape,Insulating Punching Tape,Punching Carrier Tape
ShenZhen KDW Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.smtsplicetape.com