Surface treatment techniques can be classified into the following categories depending on the method used.
First, the electrochemical method
This method uses an electrode reaction to form a coating on the surface of the workpiece. The main method is:
(1) Electroplating
(two) oxidation

In the electrolyte solution, the workpiece is an anode, and the process of forming an oxide film on the surface under the action of an external current is called anodization, such as anodization of an aluminum alloy.
The oxidation treatment of steel can be carried out by chemical or electrochemical methods. The chemical method is to put the workpiece into an oxidizing solution and form an oxide film on the surface of the workpiece by chemical action, such as bluening treatment of steel.Second, the chemical method
This method has no current action and uses a chemical interaction to form a plating layer on the surface of the workpiece. The main method is:
(1) Chemical conversion film treatment
In an electrolyte solution, a process in which a metal workpiece acts without an external current, and a chemical substance in the solution interacts with the workpiece to form a plating layer on the surface thereof is called a chemical conversion film treatment. Such as blue surface of the metal, phosphating, passivation, chromium salt treatment.
(2) Electroless plating

In the electrolyte solution, the surface of the workpiece is subjected to catalytic treatment without external current. In the solution, due to the reduction of chemical substances, certain substances are deposited on the surface of the workpiece to form a plating process, which is called electroless plating, such as electroless nickel plating. Electroless copper plating, etc.
Third, thermal processing methods
This method involves melting or thermally diffusing the material under high temperature conditions to form a coating on the surface of the workpiece. The main methods are:
(1) Hot dip plating
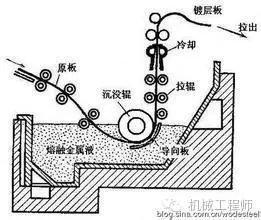
The process in which a metal workpiece is placed in a molten metal to form a coating on its surface is called hot dip plating, such as hot dip galvanizing or hot aluminizing.(2) Thermal spraying

The process of atomizing molten metal and spraying it on the surface of a workpiece to form a coating is called thermal spraying, such as thermal spraying of zinc, thermal spraying of aluminum, and the like.
(3) Hot stamping
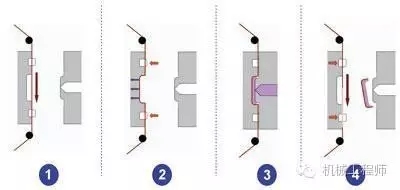
The process of forming a coating layer by heating and pressing a metal foil on the surface of the workpiece is called hot stamping, such as hot stamping aluminum foil.
(4) Chemical heat treatment
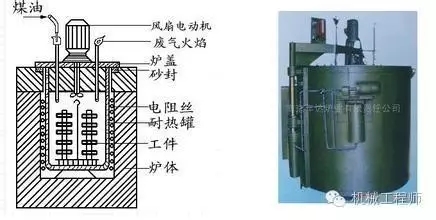
The process of contacting and heating a workpiece with a chemical substance to cause an element to enter the surface of the workpiece at a high temperature is called a chemical heat treatment such as nitriding or carburizing.
(5) surfacing
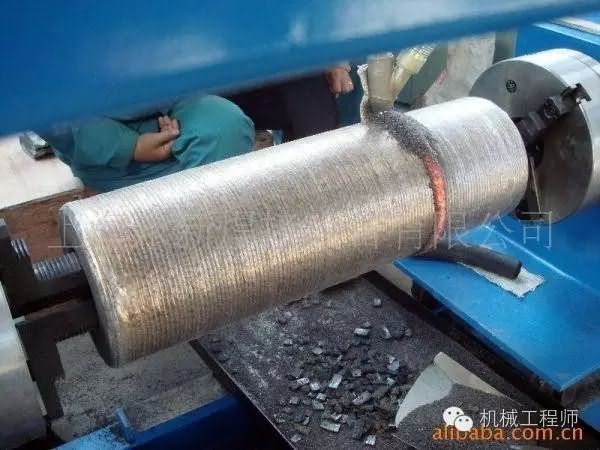

The process of forming a solder layer by welding the deposited metal on the surface of the workpiece, called surfacing, such as surfacing wear-resistant alloy.
Fourth, the vacuum method
This method is a process in which a material is vaporized or ionized on a surface of a workpiece under high vacuum to form a plating layer. The main method is.
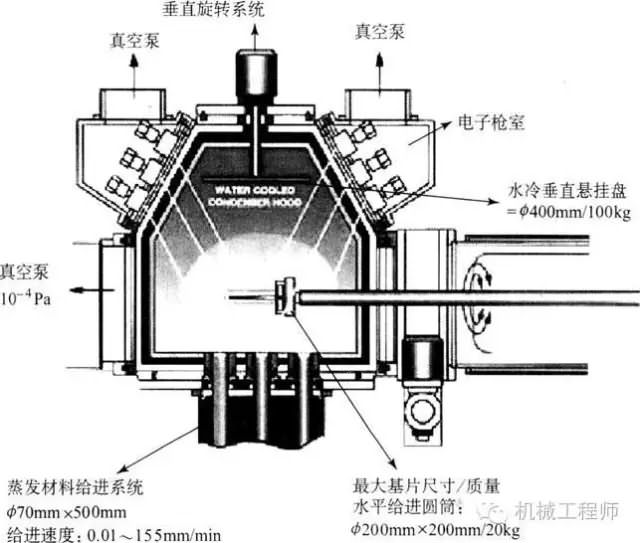
(1) Physical vapor deposition (PVD)
Under vacuum conditions, the metal is vaporized into atoms or molecules, or ionized into ions, deposited directly onto the surface of the workpiece to form a coating process, called physical vapor deposition, whose deposited particle beam is derived from non-chemical factors such as evaporation. Plating, ion plating, etc.
(2) Ion implantation
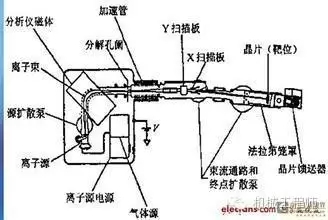
The process of injecting different ions into the surface of a workpiece at a high voltage to modify its surface is called ion implantation, such as boron injection.
(3) Chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
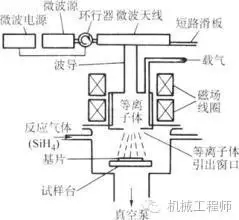
Under low pressure (sometimes also under normal pressure), the process of generating a solid deposit on the surface of a workpiece due to chemical reaction is called chemical vapor deposition, such as vapor deposition of silicon oxide, silicon nitride, and the like.
Five, other methods
Mainly mechanical, chemical, electrochemical, physical methods. The main method is.
(1) Painting

A process of applying a coating (organic or inorganic) to a surface of a workpiece to form a coating, such as painting, painting, etc., by a random spraying or brushing method.
(2) Impact plating

A method of electrodepositing a thin metal layer in a specific solution at a high current density for a short time to improve the adhesion between the plating layer and the substrate, which is called impact plating, such as impact galvanizing.
(3) Laser surface treatment

The process of irradiating the surface of a workpiece with a laser to change its structure is called laser surface treatment, such as laser quenching, laser remelting, and the like.
(4) Super hard membrane technology

The technique of preparing a superhard film on the surface of a workpiece by physical or chemical means is called superhard film technology. Such as diamond film, cubic boron nitride film.
(5) Electrophoresis and electrostatic spraying
1, electrophoresis
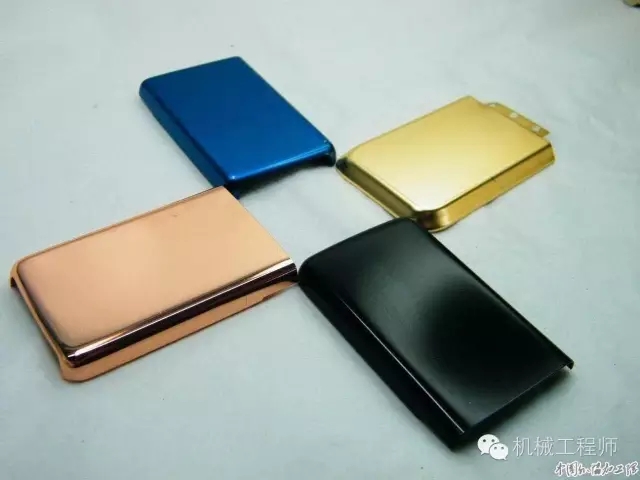

The workpiece is placed as an electrode in an electrically conductive, water-soluble or water-emulsified coating that forms a circuit with the other electrode in the coating. Under the action of the electric field, the coating solution has dissociated into charged resin ions, the cation moves toward the cathode, and the anion moves toward the anode. These charged resin ions, along with the adsorbed pigment particles, are electrophoresed onto the surface of the workpiece to form a coating, a process known as electrophoresis.
2, electrostatic spraying
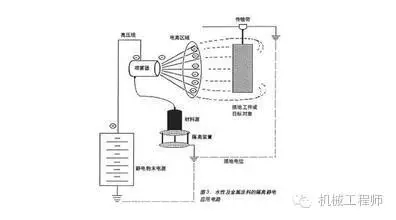
In the action of a DC high-voltage electric field, the atomized negatively charged paint particles are directed onto a positively charged workpiece to obtain a paint film process, which is called static spraying.
Chain Block 1 Ton,Chain Come Along,Chain Pulley Block,Chain Block 2 Ton
Guangdong Gongyou Lift Slings Machinery CO.,LTD , https://www.wmpallettruck.com