In cotton production, the use of herbicides and plant growth regulators is a common measure, but some use of improper or arbitrary increase in dosage, often a large area of ​​phytotoxicity, so should pay close attention.
Herbicide phytotoxicity and symptoms: including growth inhibition, stem and leaf twist, internode shortening, leaf thickening, chlorosis, whitening, dead spots, deformities and so on. For example, trifluralin and acetochlor are used for weeding in a seedbed, and a slight inadvertent cotton will suffer. The grass leaves will fade and wither the young leaves of cotton. Paraquat leaves can be discolored after 2 to 3 hours of treatment. Cotton is very sensitive to 2,4-D butyl ester, and the damaged leaves become smaller and narrower, showing a "chicken-like shape". When the damage is serious, the fruit branches cannot protrude normally.
Plant growth regulators phytotoxicity and symptoms: commonly used chlormequats, such as excessive application concentration, excessive dosage, will inhibit the growth of cotton plants, make cotton plants too short, buds are easy to fall off, and even cotton bolls become deformed. When the acetaminophen is sprayed excessively, it will inhibit its growth, and the phenomenon of dark green leaves, thick leaves, deformities, shrinkage, and short internodes will occur.
Control measures: 1. Strict operation. When using, the drug should be selected reasonably according to the operating rules, and the concentration, method and time used in the instruction manual should be read repeatedly to prevent the use of improper drug damage. 2. Clean in time. After the phytotoxicity occurs, the leaf surface can be rinsed with a large amount of water, and the soil can be washed with water or drained. 3. Neutralize and detoxify with safener, and spray 0.5%~1% lime milk to neutralize detoxification. Because "920" has the function of promoting plant cell growth, division and differentiation, when cotton produces chlormequat and ketamine, it can spray a certain concentration of "920" to relieve the phytotoxicity. Paraquat encounters the soil and is passivated and invalidated. Immediately after the accidental spraying, the method of splashing mud water can be used to make the medicine on the surface of the crop invalid. 4. Cotton field spraying equipment should be used exclusively. Sprayers and measuring cups sprayed with 2,4-D butyl ester and dimethyltetrachloride should not be used. It must be thoroughly cleaned before spraying other pesticides. 5. Strengthen the protection, use the herbicide herbicide to spray between the cotton rows, choose the windless weather, the nozzle should be equipped with a protective cover, press the nozzle when spraying, try not to spray the liquid onto the cotton. (Cao Dihuan, Rural Office of Qijiang City, Hunan Province)
Farmers Daily
Herbicide phytotoxicity and symptoms: including growth inhibition, stem and leaf twist, internode shortening, leaf thickening, chlorosis, whitening, dead spots, deformities and so on. For example, trifluralin and acetochlor are used for weeding in a seedbed, and a slight inadvertent cotton will suffer. The grass leaves will fade and wither the young leaves of cotton. Paraquat leaves can be discolored after 2 to 3 hours of treatment. Cotton is very sensitive to 2,4-D butyl ester, and the damaged leaves become smaller and narrower, showing a "chicken-like shape". When the damage is serious, the fruit branches cannot protrude normally.
Plant growth regulators phytotoxicity and symptoms: commonly used chlormequats, such as excessive application concentration, excessive dosage, will inhibit the growth of cotton plants, make cotton plants too short, buds are easy to fall off, and even cotton bolls become deformed. When the acetaminophen is sprayed excessively, it will inhibit its growth, and the phenomenon of dark green leaves, thick leaves, deformities, shrinkage, and short internodes will occur.
Control measures: 1. Strict operation. When using, the drug should be selected reasonably according to the operating rules, and the concentration, method and time used in the instruction manual should be read repeatedly to prevent the use of improper drug damage. 2. Clean in time. After the phytotoxicity occurs, the leaf surface can be rinsed with a large amount of water, and the soil can be washed with water or drained. 3. Neutralize and detoxify with safener, and spray 0.5%~1% lime milk to neutralize detoxification. Because "920" has the function of promoting plant cell growth, division and differentiation, when cotton produces chlormequat and ketamine, it can spray a certain concentration of "920" to relieve the phytotoxicity. Paraquat encounters the soil and is passivated and invalidated. Immediately after the accidental spraying, the method of splashing mud water can be used to make the medicine on the surface of the crop invalid. 4. Cotton field spraying equipment should be used exclusively. Sprayers and measuring cups sprayed with 2,4-D butyl ester and dimethyltetrachloride should not be used. It must be thoroughly cleaned before spraying other pesticides. 5. Strengthen the protection, use the herbicide herbicide to spray between the cotton rows, choose the windless weather, the nozzle should be equipped with a protective cover, press the nozzle when spraying, try not to spray the liquid onto the cotton. (Cao Dihuan, Rural Office of Qijiang City, Hunan Province)
Farmers Daily
ã€Comment】 ã€Print this article】 ã€Close this page】 ã€Large, medium and small】
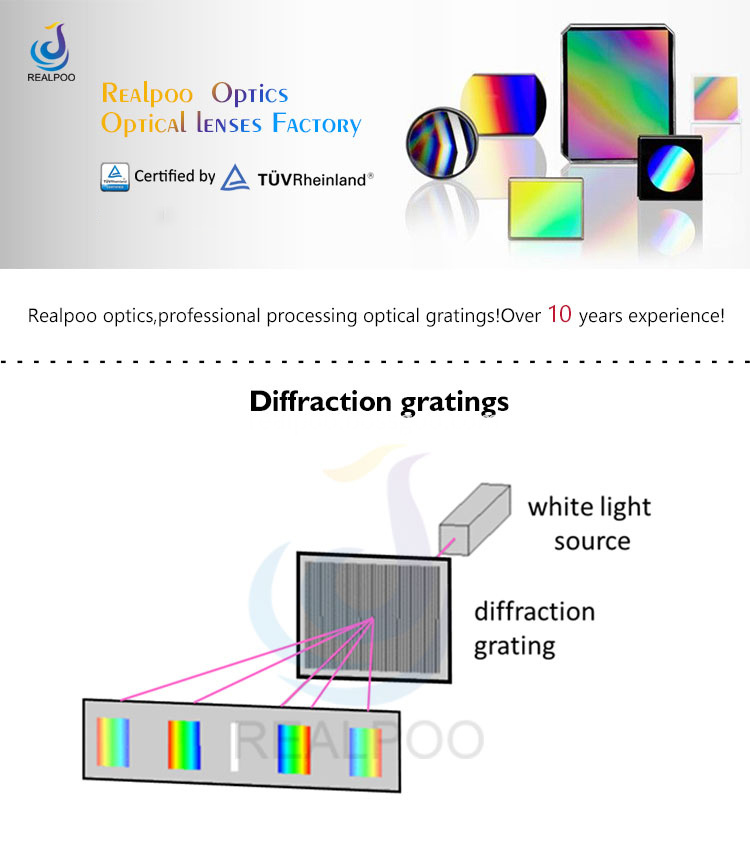
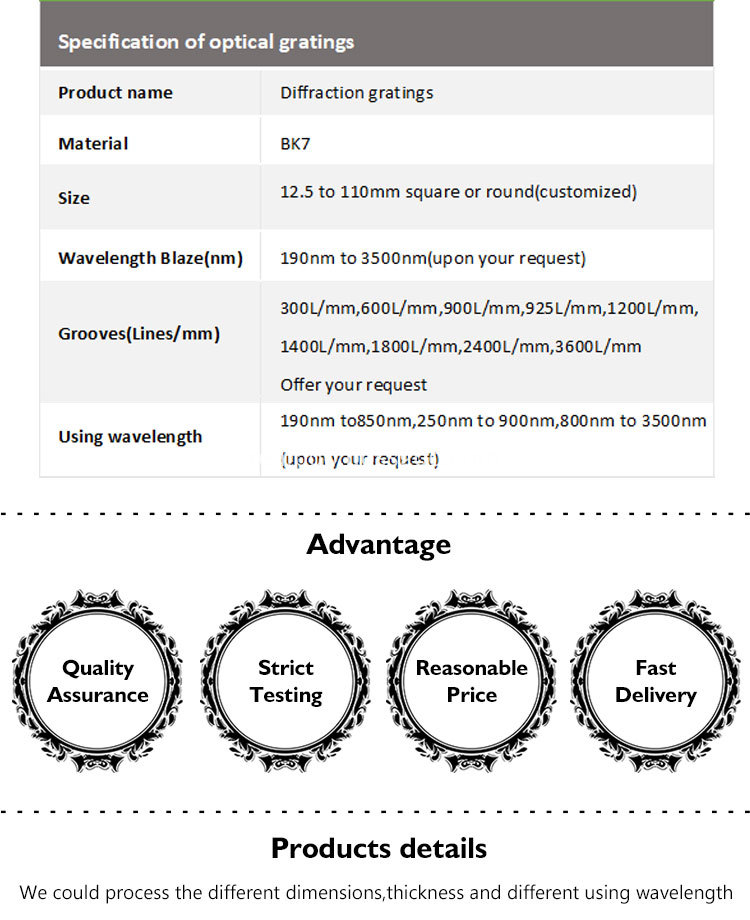
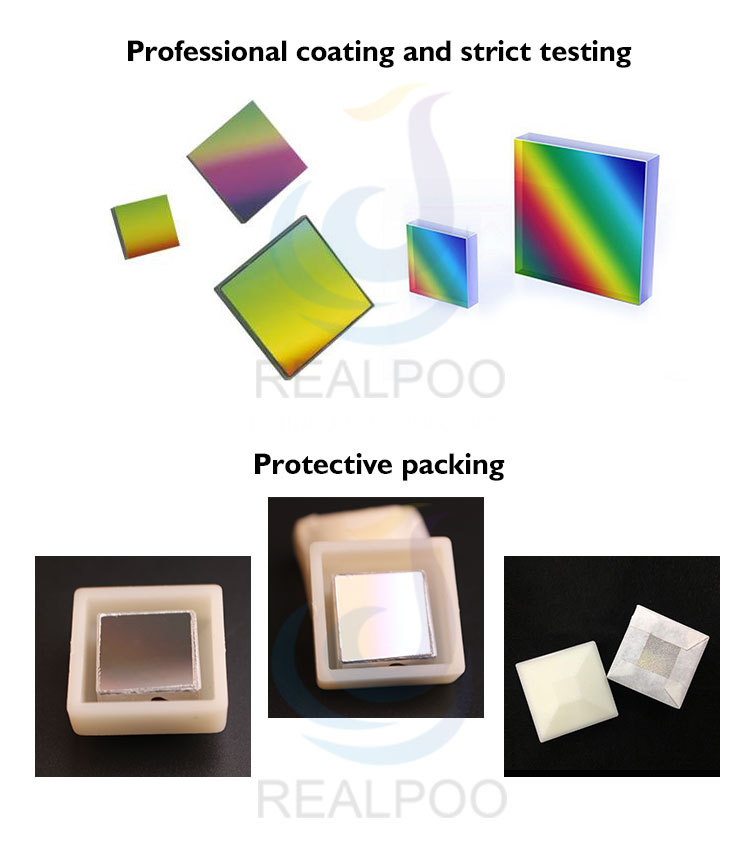

Diffraction Grating,Diffraction Gratings,Grating Optics,Holographic diffraction grating, Holographic Grating
Changchun Realpoo Photoelectric Co., Ltd. , https://www.optics-realpoo.com